Good good study, day day up
Section1: Coordinate system
Section2: The Milky Way Galaxy (p. 1044)
First, the structure of the Galaxy.
Different views:
Face-on: usually no jet.
Edge-on
Pole-on: view along with the jet.
the difference of face and pole on depends on the object and celestial.
Alpha Centauri---有大项目计划send explorer去
We are in Globular Cluster? right?
Galactic coordinate 银道坐标
Use the Galactic structure as a reference frame.
The distance of solar system to GC is about 8.0 kpc --> Galactocentric distance (银心距)
Galactic longitude 银经 (l)
Galactic latitude 银纬 (b)
详情请看图:
- unit usually use degree.
- 银道坐标系中心应当是地心!!图里的center只是表示银心~
The direction of th Galactic rotation (银河自转)
由北pole向下face on,顺时针旋转,一周的时间约250 million yr. (Clockwise as we see from the North Pole)
Galactic bulge(星系核球)
What is Stellar halo(恒星晕)?
Conversion between galactic and equatorial coordinates
--> Just change the direction of the axis:
The Galactic Center (G.C.) in J2000.0 G.C. is at , for equatorial system are:
当银道坐标系上两颗星过近时,通常可定义为:
double stars
binary stars
Conversion tools:
- HEASARC Coordinate Converter
- Astropy.Coordinates
Note: angular distance on a celestial sphere
由于球面所带来的计算误差,不能简单地使用勾股定理!
Section3: Conclusion of the last class and so on.. --> Time systems used in astronomy
what is sidereal time? -->恒星时
diurnal[daɪˈɜːrnl] motion-->周日运动
G.C. : Sgr
Q: What is the angular separation of the closest possible double star?
- This depends on the angular resolution of the telescope
- Two main factors determing the angular resolution of the telescope (p. 168)
- Seeing (视宁度): Sgaroness of a telescopic image. Seeing depends on the degree of turbulence in the Earth's atmosphere at telescope sites. ~0.1'' in the best case (in the case of optical)
- Diffraction limit (衍射极限): Theoretical limit of angular resolution due to wave nature of light. , more detail plz see here
Radial velocity : 径向速度(视向速度)
Transverse velosity : 切向速度
Boltzmann ditribution:
Additional note on transitions
- Electronic transition (电子跃迁)
- Energy: optical, ultraviolet, shorter wavelength
- Vibrational transition (振动跃迁)
- Energy (hv): intrared
- Rotation transition (转动跃迁)
- Energy: Radio
- Hyperfine transition (超精细跃迁)
- Energy: Radio (very long )
了解一下望远镜干涉远离(信息丢失?信息复原,衍射原理)
2021.9.18
---- Good question on the beginning😀
Solar time (太阳时)
- The time sytem based on the Solar position
- Noon (12pm) in the Solar time is
- the annually averaged time of the Solar meridian passage
- Note: meridian passage = 中天
Sidereal time (恒星时)
- The time system based on the positions of stars
- Noon (12pm) ....
恒星日比太阳日要短!因为地球公转,详情看图:
Common year 平年 --- 1/4 day shorts of a complete orbit
Leap year 闰年 +3/4 day over a complete orbit
Tropical year 回归年 ---One complete orbit around the Sun
Local standard time (LST)
Universal time (UT, GMT)
-The mean solar time at the Greenwich meridian(LONGITUDE = )
Julian day (儒略日)
Time-variation plot with date (年月日, i.e., Gregorian calendar) on horizontal axis
---not ez for observer
Why dont use 年月日?
- Numerical analysis is not ez
- Difficult to read the number of days
- Leap year
So in astronomy, we use Julian day
What is Julian day?
- Julian day (JD) is the total number of days from JD 0.0
- JD 0.0 is defined as
- the noon (UT) on Jan, B.C. 4713, why Noon??
- bcz Day doesnt change in the night
- Examples
- Noon (UT) on 1st Jan 2000 is JD 2,451,545.0
- 6pm (UT) on 1st Jan 2000 is JD 2,451,454,25
- Today now is (Sep 2021, 11h40m0s CST) JD 2459476.31944
Modified Julian Day (MJD) MJD=JD-2400000.5
Note: MJD starts at midnight
Heliocentric(以太阳为中心的) Julian Day (HJD)
Practice a bit
(1) Calculate Julian Day for September 2021 1pm CST
(2) What is the corresponding modified Julian day (MJD)?
Homework next week:
UT
UTC
GMT
CST
ST clock
UT clock
and how to transform from UT to ST?
Assignment:
解释一下:
- 什么是太阳时和恒星时
- 为何天文台里需要使用恒星时ST
- 如何转换UT to ST?
Trying to explain :
- What is Solar Time and Sidereal Time (st)?
- Why observatory use ST time?
- How to transform from UT to ST?
在开始之前(Before the beginning):
Sidereal time 是基于恒星的, 这个恒星不是太阳的意思,而是除太阳外的恒星,或是一些深空天体,比如星云或者类星体等(详情可见here)
Sidereal time bases on STAR, and this "STAR" is not the Sun, but some other stars, or some deep space objects, like Nebula or Quasar (see more detail at here)
一些常用缩写的定义 (Definitions of some frequently used acronyms):
UT: Universal Time (reflect the Solar time, the duration from one solar noon to next)
UTC: Coordinated Universal Time (leap second, subset of UT)
GMT: Greenwich Mean Time (time zone)
CST: China Standard Time (UTC/GMT+8)
第一个问题(The question):
看图即可心领神会~
Just follow the illustration is enough ~
💁该动画原链接
💁The url of this animation is Link
第二个问题(The question):
- 当某一物体经过中天点的时候,当地的LST时间即是该物体的赤经,贼方便。
- 太阳时是根据太阳来的,而恒星时是根据(star)来的,更准直,可以更好地抵消地球公转带来的影响
- When a celestial object passes the meridian passage point, the time of LST is the RA of the object, its really convenient for astronomer.
- Solar time is based on our Sun, and Sidereal time is based on star, the latter is more collimated, can moderately omit the influence of the Earth revolution.
第三个问题(The question):
上图参考(懒得算了😅)
Please just follow the picture below.
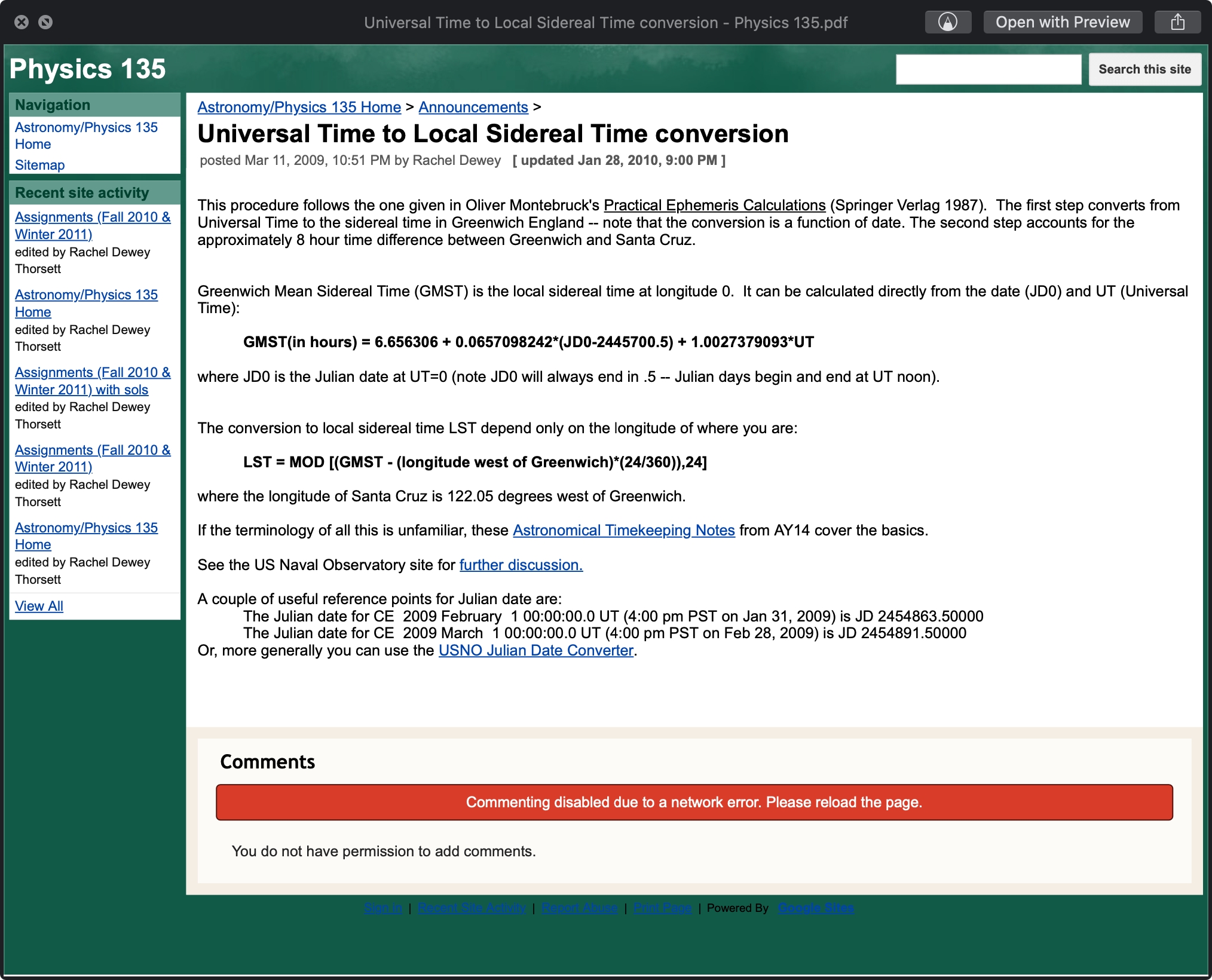
💁该图片原网页
💁The source page of this picture Web
上课的presentation下载地址:点我
Section3~4 (follow-up 2021.9.22): Distance unites used in astronomy
Julian Day Calculator: https://www.aavso.org/jd-calculator
-->See, 3. The continuous spectrum of light in the textbook
-
Light year
1 tropical year!!! -
Astronomical Unit (AU, 天文单位)
Averaged distance between the Sun and the Earth
(Note: )
Fundamental of the distance unit used in astronomy -
Trigonometry
Trigonometry (三角测量) is the distance measurement method using the trigonometric parallax (三角视差)
Concepts: B: base line (基线), p: parallax angle (视差角) -
Trigonometry in Space
In priciple, we can measure the distance to stars with trigonometry, but stars are very far away.
So, we need a long baseline to see the parallax angle.
-
Definition of parsec
Parallax angle is very small,
Therefore,
So, the formula can be approximated as follows:Since,
We can convert the angle from rad to arcsec as follows:So, the distance formular can be changed as follows:
Therefore, when p''=206,264.806 [AU}, the
With this definition, the distance formula can be changed as follows:
-
Summary of parsec
- The distance at which 1 AU subtends (对着) an angle of 1''
- Relation with "light year", 1 [pc]=3.26[ly]
- Examples:
Centauri (The nearest star to us) ~ 1.3 [pc]
-
Relation between parallax angle and parsec
The relationship between parallax angle (p'') and distance (d) is beautifully obcvious. -
Exercise a bit
solution:so we have, =6039.43351968km
Nakashima's answer: annular parallax angle is
Little small discussion:
How to measure 1 AU?
2021.9.26-27 Continue at last lecture....
上节课的总结与改正:
Brief introduction of Maser:
本质:玻尔兹曼分布布居数反转!!
Boltzmann distribution:
Process: pumping radiation(泵浦辐射,水泵现象),造成布居数反转。
附赠中岛手绘:
关于利用金星测量太阳距离:
cm is used due to the good reflection rate.
cm used to investigate the Venus atmosphere
所以,测距使用的并不是Laser Ranging (激光测距) 而是 Radar Echo (雷达回波)
星系没有一个确切的边界,边界是由Scale height来定的
Scale height H:
z: distance from the disk
: number density of stars at z=0
P: number density of stars at z
Continue on ..
Elongation(距角): The angular distance(这是一个角度,而不是距离) separating the Moon or a planet from the Sun
Venus at the greatest eastern elongation (东大距)----evening
At the greatest western elongation (西大距) ---- in the morning
How to obtain the Galactic rotation curve from gas?
We can derive the Galactocentric distance and radial velocity of the gas component at tangential point D.
VLBI --- 限于看小angular distance,高亮的源,可参考Fourier Transform.
Section 5: The Magnitude Scale
(see, "3. The Continuous Spectrum of Light" in the textbook)
Apparent magnitude (视星等)
--> Basic idea formed in ancient Greek
(1 mag difference (m=1))=(a factor 2.512 times in brightness)
for instance, m=2, factor is ....
How many times different above two magnitudes in brightness?
answer:
课堂小知识:
import numpy as np
L=3.839*10**26
r=1.496*10**11
S=4*np.pi*r**2
flux=L/S
print(flux)
2021.9.29
minor次要的
Qualitative introduction of radio interferomerry EHT
- Short baselines are sensitive to large stucture
- Long base lines are sensitive to small structure
THe interferometer is mathematically the Fourier transform.
Limited number of antennas cannot completely reproduce the source structure
二维傅立叶变换,反映的是梯度Gradient! --> 空间频率+相位图
fringe pattern-->条纹图案
deconvolve-->去卷积
- The true emission should not change in shape if we use different CLEAN box sizes.
Jansky
1 Jy =
2021.10.11
Distance modulus
--> 距离模数:
m-M is mathematically equivalent to the distance:
so far, we have assumed that there is no interstellar extinction!!
Interstellar extinction (星际消光)
Here we define interstellar extinction :
interstellar extinction depends on the wavelength! 河内和外都会有,主要集中在光学波段
Some more details on radio interferometry
visibility=brightness fringe pattern
point spread function: 点扩散函数
CLEAN algorithm
- CLEAN is the dominant deconvolution algorithm in radio astronomy.
Initial step:
- Identify the highest peak in the dirty map as a point source.
- Subtract a fraction of this peak from the residual map using a scaled dirty beam
- Add this point source location and amplitude to Clean Component list (https://2199k.cn/post-images/1633922962928.JPG)
- Go to step 1 (an iteration) unless stopping criterion reached
- Stopping criteria:
- Residual map maximum < threshold =several X rms
2021.10.13
References for further study of radio astronomy.
- Essential Radio Astronomy
- Interferometry and Synthesis in Radio Astronomy
- NRAO Systhesis ...
- CASA ...
Black body radiation
jargon:行话
Neutrinos doenst belong to** Cosmic rays**---> because Cosmic rays are electrul charged.
中岛的长无线电波手绘🐢:
Stefan-Boltzmann law:
where is effective temperature.
Plank's law 波长到频率的转换参考:

Key procedure:
Revelation:
- If we know the equation , then we can:
and
So, in the case , this form becomes like:
so we have finally:
Rayleigh-Jeans --> 右边
Wien --> 左边
Effective temperature: T calculated under the assumption of black body radiation.
Note that effective temperature not always represent the True temperrature.
2021.10.18
Maser pumping mechanism
- Collisional pumping
- Collision with ambient molecules
- This often happens in interaction regions between two kinematic componnets
- Radiative pumping
- Radiation from a star etc. (SiO maser in evoleved starts)
- Line over lapping
Photometric bands and color index #1
Section 7, (see, "3. The continuous spectrum of light" in textbook)
Photometry and photometric band
In the reality, the usually the intensity is measured in a certain range of .
The wavelength ranges used for photometry are called photometric bands
We use a "filter" to limit the wavelength range.
Filter can pass the radiation only a certain range of .
Johnson-Cousin UBVRI system (3000-9000):
- CCD arrays enable us to do imaging and photometry at one time
Color index
The apparent and absolution magnitudes can be defined for each photometric band.
U, B, V can be measured separately
: passband characteristics of the U band filter.
The difference in magnitude like U-B and B-V is called "color index"
As we see above, color is independent of distance !!!
2021.10.20
Color temperature
The color index U-B equals to a ratio of flux values at U band B-bands:
So, the color index uniquely determines the effective temperature.
--> color is relying on effective temperature
Color index #2
HR (Hertzsprung-Russell) diagram.
对于O型恒星,很多电子跑路了,所以spectral feature is weak.
Bolometric correction
Section 9
- Definition of the bolometric correction
- Meaning of the bolometric correction
- Possibly, could be a useful tool to obtain the total energy emitted from source
- Limitation of the bolometric correction
The bolometric correction BC is defined as follows:
: apparent bolometric magnitude
: apparent V-band magnitude
"bolometric" means "total energy" over "all" wavelength
Meaning of the bolometric correction
If we know BC, we can convert to
For instance, for bright(nearby) stars, and V are measure, and BC is determined.
Then, the obtained BC is applied for similar stars, which possibly show the similar SEDs.
BC always taks a negative value, because flux for is larger than that for
Limitation of the bolometric correction
- It is often impossible to properly measure , because the photometric system doesnt cover entire SED.
- SEDs are not completely the same even among the stars with the same spectral type.
2021.10.25
Color excess
"color" is altered by extinction, and this effect on color is called "color excess" or "reddening"
The color excess isimportant from 2 viewpoints:
- Calculating the distance of a certain object
- Investigating the properties of interstellar materials.
The color excess isquantitively defined as follows:
where is not minus, but a funtion !!
Using , the above formula can be written as follows:
is in proportional to :
The procedure to derive :
2021.11.8
Intensity
Prove that specific intensity is independent of distance:
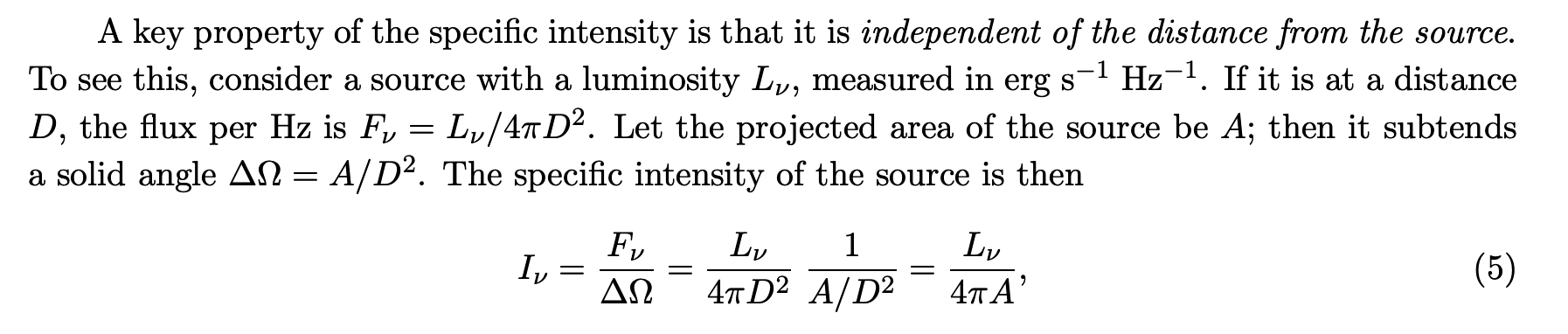
心得: 需要注意的是,像 这种量,放在积分里面才会有其"单位"立体角的数学物理意义,单独放在外面不能简单认为是1sr里面的Intensity
并且,的深层次理解“一束光”的能量,则不是直接从单位量纲的定义中得到,而是需要如上述的证明。
完全理解上述证明之后,则可下意识认为其来自于“一束光”。
Defining flux and luminosity
- Section 12, Based on Section 2.1 in ERA(Essential Radio Astronomy)
Specific flux=Flux density=Spectral flux
1 [Jy]= []
通常用于Structure is resolved;
通常用于Structure is not resolved.
2021.11.10
Optical depth and Radiative trasfer equation
- Section 13, Based on Section 2.2 in ERA(Essential Radio Astronomy)
--> linear absorption coefficient
Only consider absorption:
Key formula:
Optical depth :
Contribution from emission:
: emission coefficient
Intro to thermal equilibrium (TE)
Under TE, is the black body radiation:
Kirchhoff's law":
(此处关系的推导可参阅中岛的ppt)
The Planck function does not depend on material, so under TE, the dependency on material is cancelled out.
深入理解下图:
Simple applications of radiative transfer:
Section 15
(Based on Section 2.2.3 in ERA)
Brightness temperature
When , the black body radiation is approximated by the Rayleigh-Jeans law,
Then the temperature T is calculated to be :
Even if we replace with mathematically T can be calculated:
is called "brightness temperature"
not a real physical temperature, but often the indicator of
System temperature
The sum of all noises, which is converted to the temperature scale [K], is called the system temperature ()
Observation to determine
Source function:
2021.11.15
Emission or absorption
bg: background
fg: foreground
if , emission line is formed
if , absorption line is formed
Line radiative transfer fundamental
Section 17, see e.g., ERA 7.3
......
Q&M: How can we describe the microscopic phycsical processes in the equation of RT?
New concepts:
- Profile function:
- Radiation energy corresponding to the line:
- Einstein coefficients:
***Only need to know one Einstein coefficient, and another two can be derived.
理解如下图:
2021.11.17
Excitation temperature
Section 18
ERA 7.4
Defination: T dericed from Boltzman equation, not real temperature.
Q: what is Boltzman distribution?
point at LTE
Polarization fundamental
Section 19
See. e.g., ERA 2.3
好好理解Stokes参数~